While the sort function in Python is extraordinarily convenient for sorting lists. There are conditions where you may want to implement your own sorting algorithm from scratch. This might be for instructional purposes, to understand the inner workings of sorting algorithms, or to create a custom sorting behavior that the sort feature doesn’t offer.
Here are many sorting algorithms you can implement in Python without the use of the any kind of built in function:
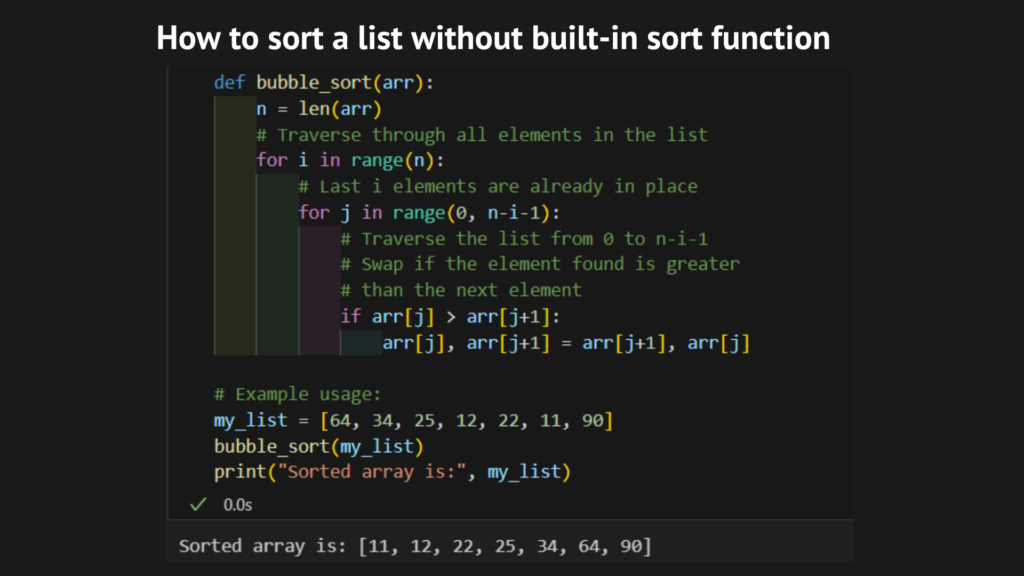
Sorting a list in python without sort function using bubble sort
def bubble_sort(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Traverse through all elements in the list
for i in range(n):
# Last i elements are already in place
for j in range(0, n–i–1):
# Traverse the list from 0 to n-i-1
# Swap if the element found is greater
# than the next element
if arr[j] > arr[j+1]:
#Swap code
arr[j], arr[j+1] = arr[j+1], arr[j]
my_list = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
bubble_sort(my_list)
print(“Sorted array is:”, my_list)
We begin by looking at the first number inside the list.
We compare subsequent numbers in a list. If the first number is bigger than the second number, we swap them. We continue doing this as we circulate through the list. The biggest numbers gradually move to the end, and the list becomes sorted
The time and space complexity of bubble sort is O(n²) and O(1) respectively.
Sorting a list in python without sort function using selection sort
def selection_sort(arr):
n = len(arr)
# Traverse through all elements in the list
for i in range(n):
# Find the minimum element in the unsorted part of the list
min_index = i
for j in range(i+1, n):
if arr[j] < arr[min_index]:
min_index = j
# Swap the found minimum element with the first element
arr[i], arr[min_index] = arr[min_index], arr[i]
# Example usage:
my_list = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
selection_sort(my_list)
print(“Sorted array is:”, my_list)
Step 1 is locating the smallest element:
- Initially, we consider the whole list as unsorted.
- Initial List: [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
- We start by searching the smallest number in the unsorted part of the list, which is 11.
- Once we get the smallest number, we swap it with the first number in the list.
- Now, the list looks like this: [11, 34, 25, 12, 22, 64, 90]. The first element is sorted.
Step 2 is finding the next smallest element:
- Next, we move to the remaining unsorted part of the list, excluding the first element (11).
- Among [34, 25, 12, 22, 64, 90], the smallest number is 12.
- We swap 12 with the second element in the list.
- Now, the list looks like this: [11, 12, 25, 34, 22, 64, 90]. The first two elements are sorted.
We repeat this process till we get a sorted list.
The time and space complexity of select sort is O(n²) and O(1) respectively.
Conclusion
We saw how to sort a list in python without the sort function using bubble sort and selection sort. Algorithms have time and space complexity. The choice of algorithm for a particular task depends on data size, desired performance, and available memory.
You can find the above code on GitHub .
You can explore our list comprehension blog which would improve your coding skills.